What Is A Consumer In Science

Ecology Consumer Definition Explanation Video Lesson Transcript Study A consumer is an animal that cannot make its own energy and relies on other organisms to survive. consumers are categorized by their food source into four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Types of consumer. 1. primary consumers. herbivores are the dominant consumers. their food source is the first trophic level in the food web, which consists of plants. plants are also considered autotrophs. autotrophs make their own energy from sunlight and basic nutrients through photosynthesis; the phrases producer and autotroph have the same.

Consumer And Producers Examples Kids Consumer science is the interdisciplinary study of how people acquire, use, and dispose of goods and services. it helps businesses understand their customers, governments protect consumers, and consumers make informed decisions. Group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. molecule. Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers, which are herbivores that eat plants. secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores, and they are important for the food chain and energy flow in ecosystems.
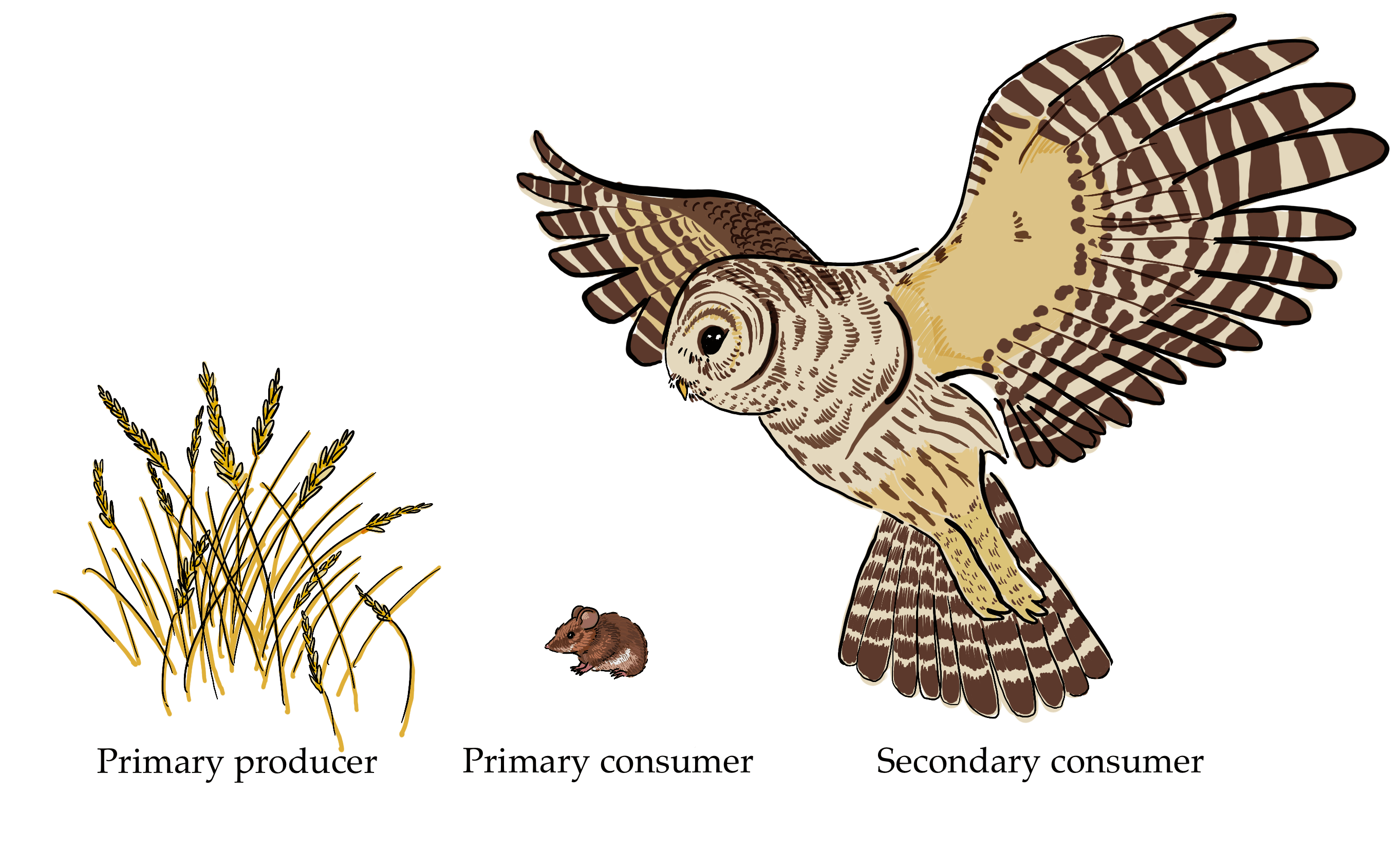
Consumer Examples Biology Marine food webs. resource. add to collection. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers, which are herbivores that eat plants. secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores, and they are important for the food chain and energy flow in ecosystems. A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers, which are autotrophic plants that produce their own food through photosynthesis. learn about the different types of primary consumers, their feeding strategies, adaptations and examples, such as ruminants, zooplankton and herbivorous birds. Consumers, or heterotrophs, are organisms that consume other organisms to obtain their energy. most organisms get energy from the sun either directly or indirectly. for example, plants, algae, and.

Comments are closed.