What Is A Consumer In A Food Web
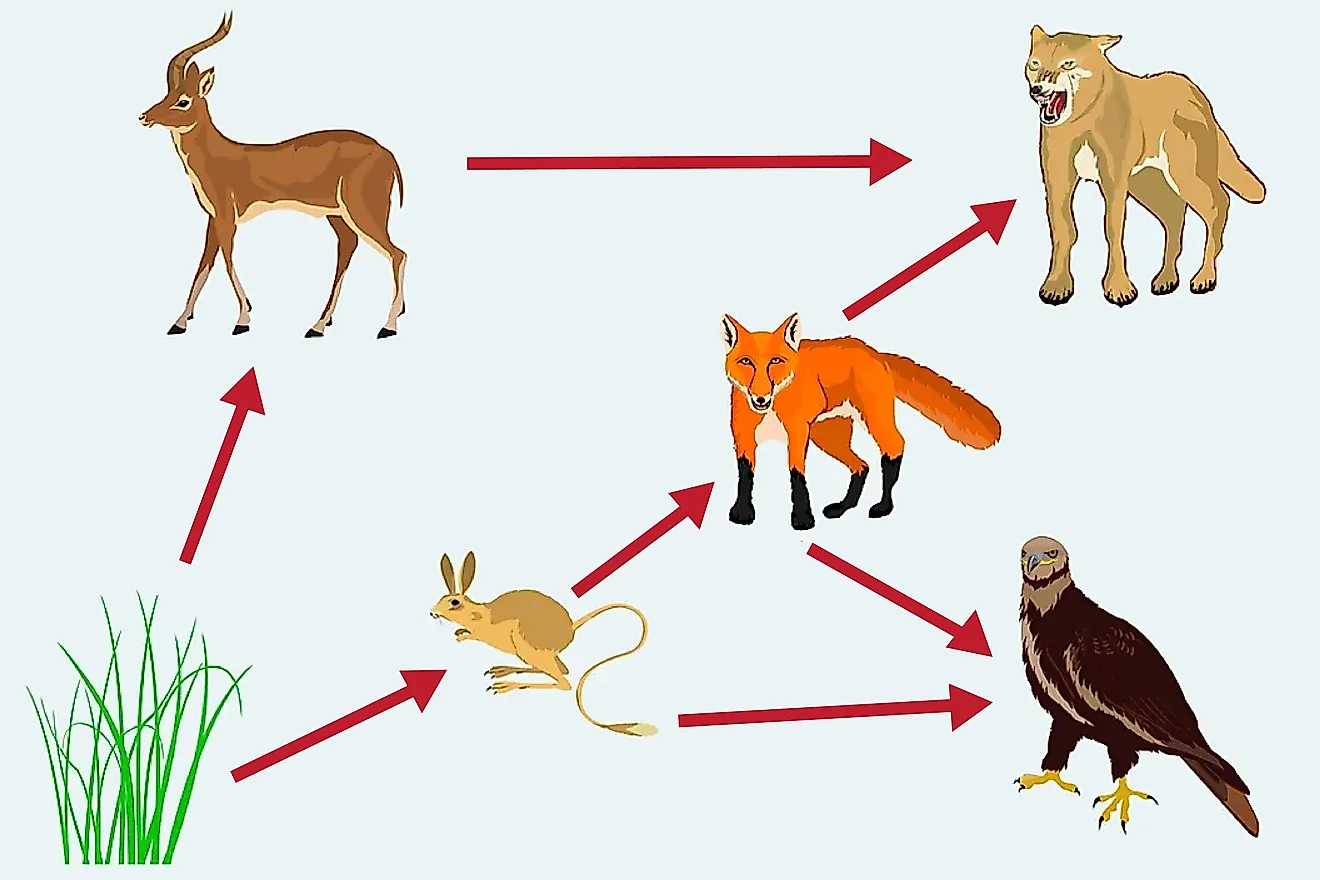
What Is A Food Web Worldatlas Examples of primary consumers are zooplankton, butterflies, rabbits, giraffes, pandas and elephants. primary consumers are herbivores. their food source is the first trophic level of organisms within the food web, or plants. plants are also referred to as autotrophs. A food chain is a network of links in a food web. here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms.
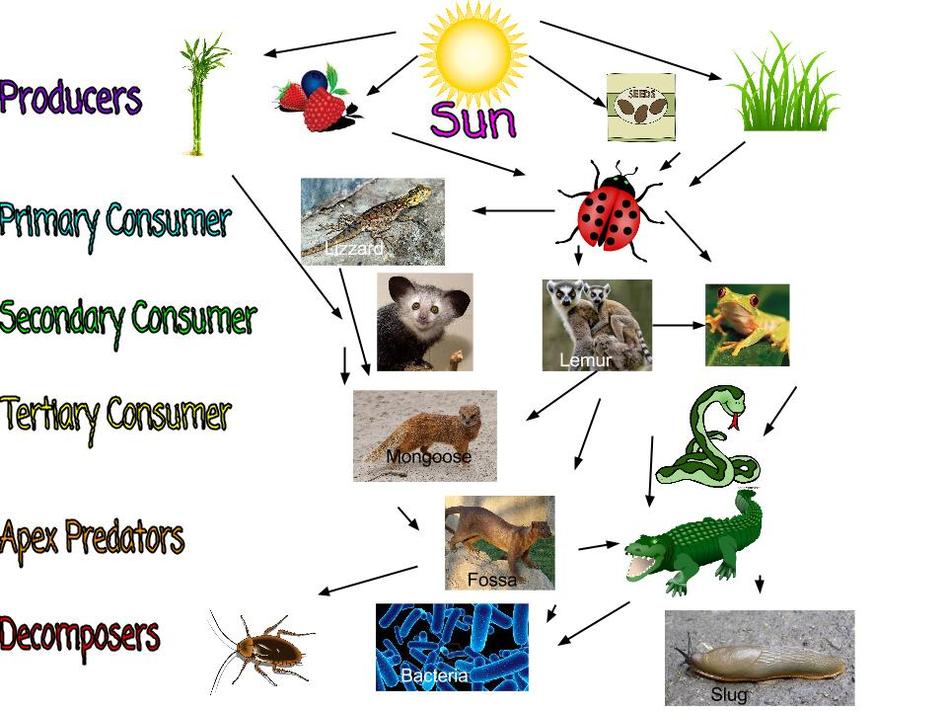
Food Web Makensie A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. within this broad designation are five main trophic levels: primary producers, primary consumers, secondary. The above is an example of the food chain, which is only a part of the food web. in another part of the food chain, a caterpillar (primary consumer) eats the leaves of plants (producers) which are eaten by birds like sparrows (secondary consumer). A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.
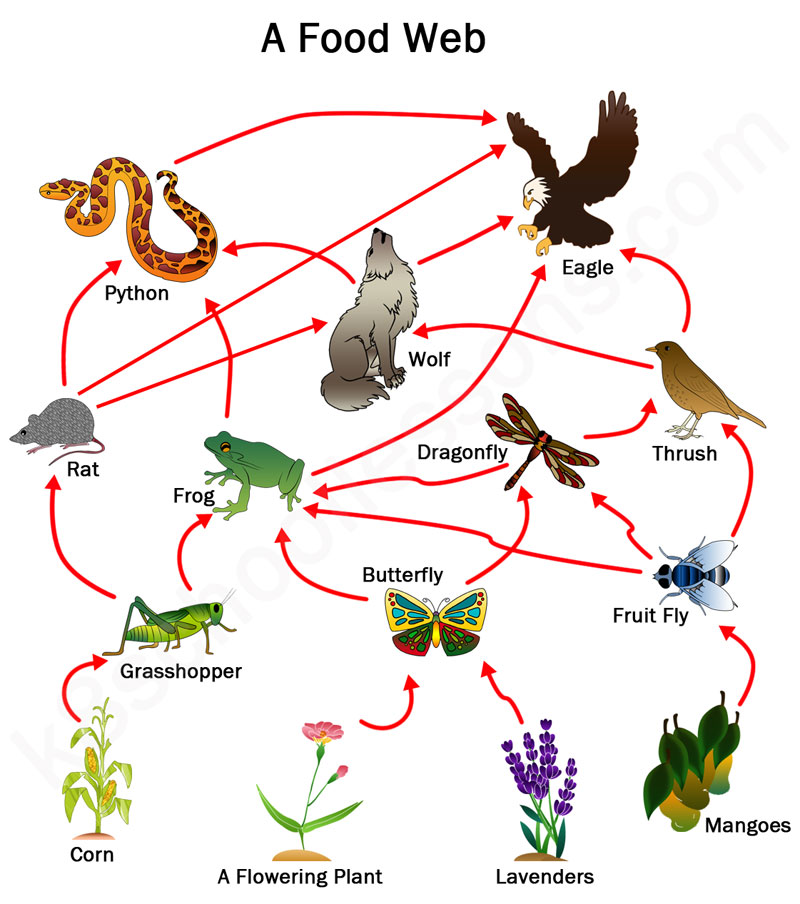
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs The above is an example of the food chain, which is only a part of the food web. in another part of the food chain, a caterpillar (primary consumer) eats the leaves of plants (producers) which are eaten by birds like sparrows (secondary consumer). A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. molecule. A million to one marine food webs are usually longer than terrestrial food webs. scientists estimate that if there are a million producers (algae, phytoplankton, and sea grass) in a food web, there may only be 10,000 herbivores. such a food web may support 100 secondary consumers, such as tuna.
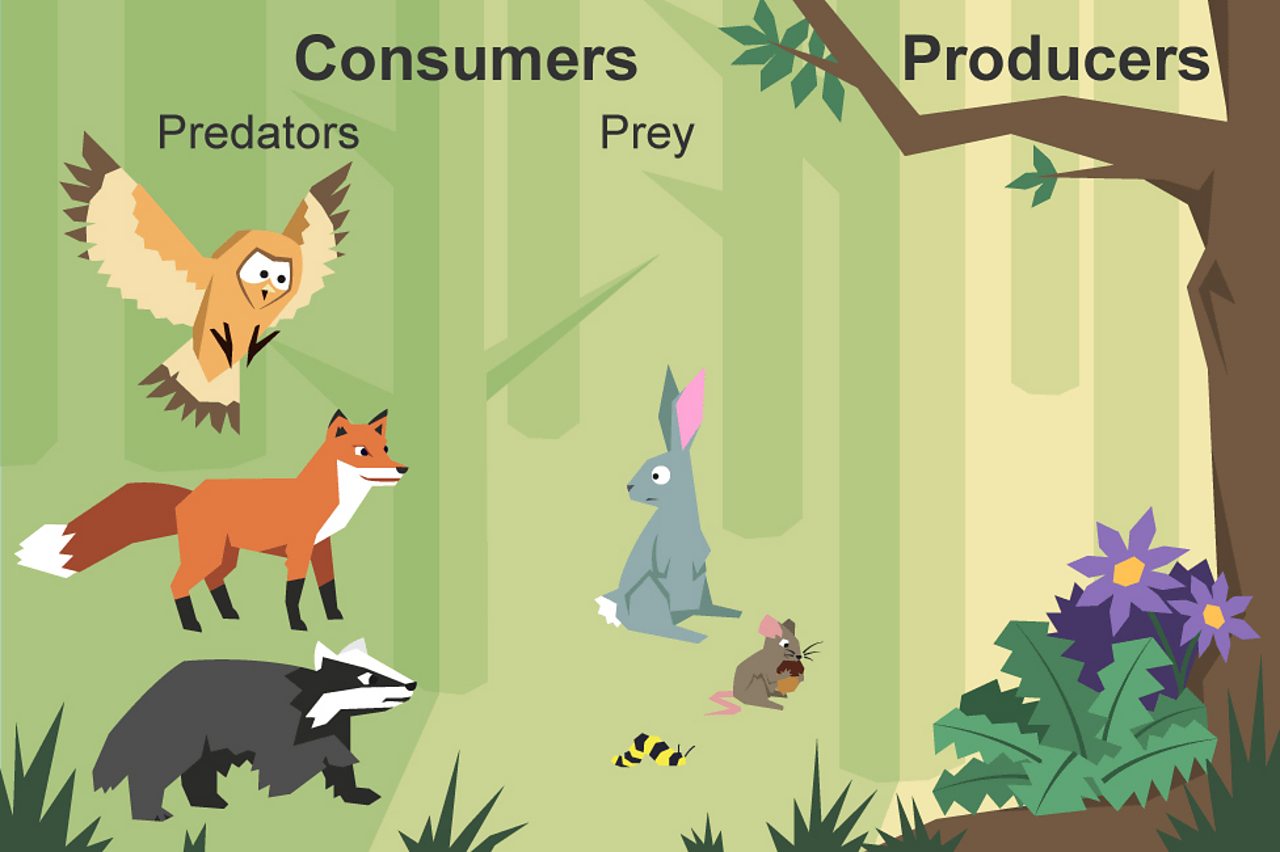
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. molecule. A million to one marine food webs are usually longer than terrestrial food webs. scientists estimate that if there are a million producers (algae, phytoplankton, and sea grass) in a food web, there may only be 10,000 herbivores. such a food web may support 100 secondary consumers, such as tuna.

Comments are closed.