Vitamin E Sources Benefits And Role Of Vitamin E In Immunity
Vitamin E Sources Benefits And Role Of Vitamin E In Immunity Abstract. vitamin e is a fat soluble antioxidant that can protect the polyunsaturated fatty acids (pufas) in the membrane from oxidation, regulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ros) and reactive nitrogen species (rns), and modulate signal transduction. immunomodulatory effects of vitamin e have been observed in animal and human. Clinical relevance of vitamin e in the regulation of immune function. evidence from animal and human studies has demonstrated that the immunoregulatory role of vitamin e is associated with reducing risk for infectious diseases such as respiratory infections, as well as some allergic diseases such as asthma.
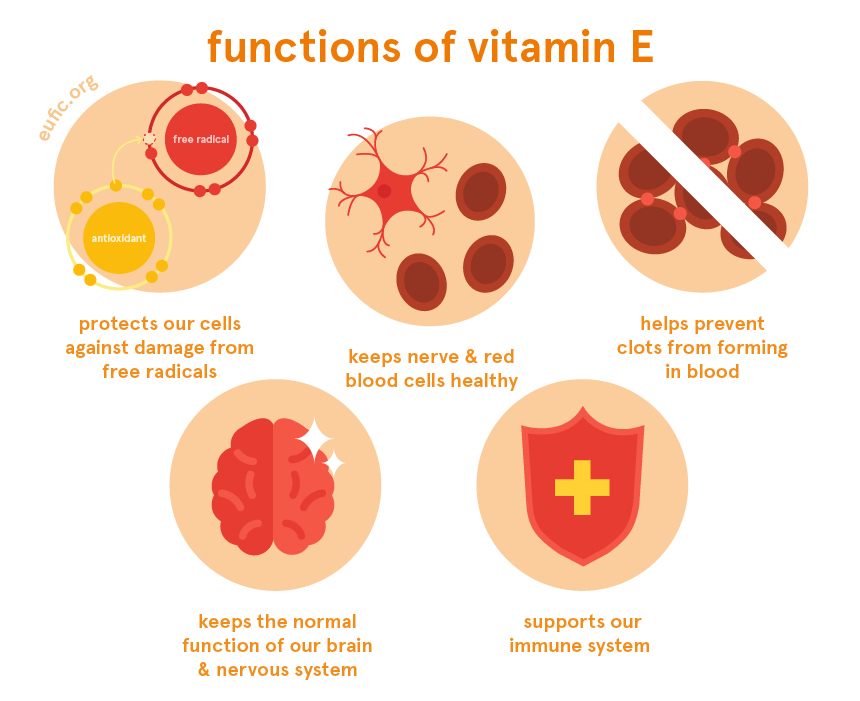
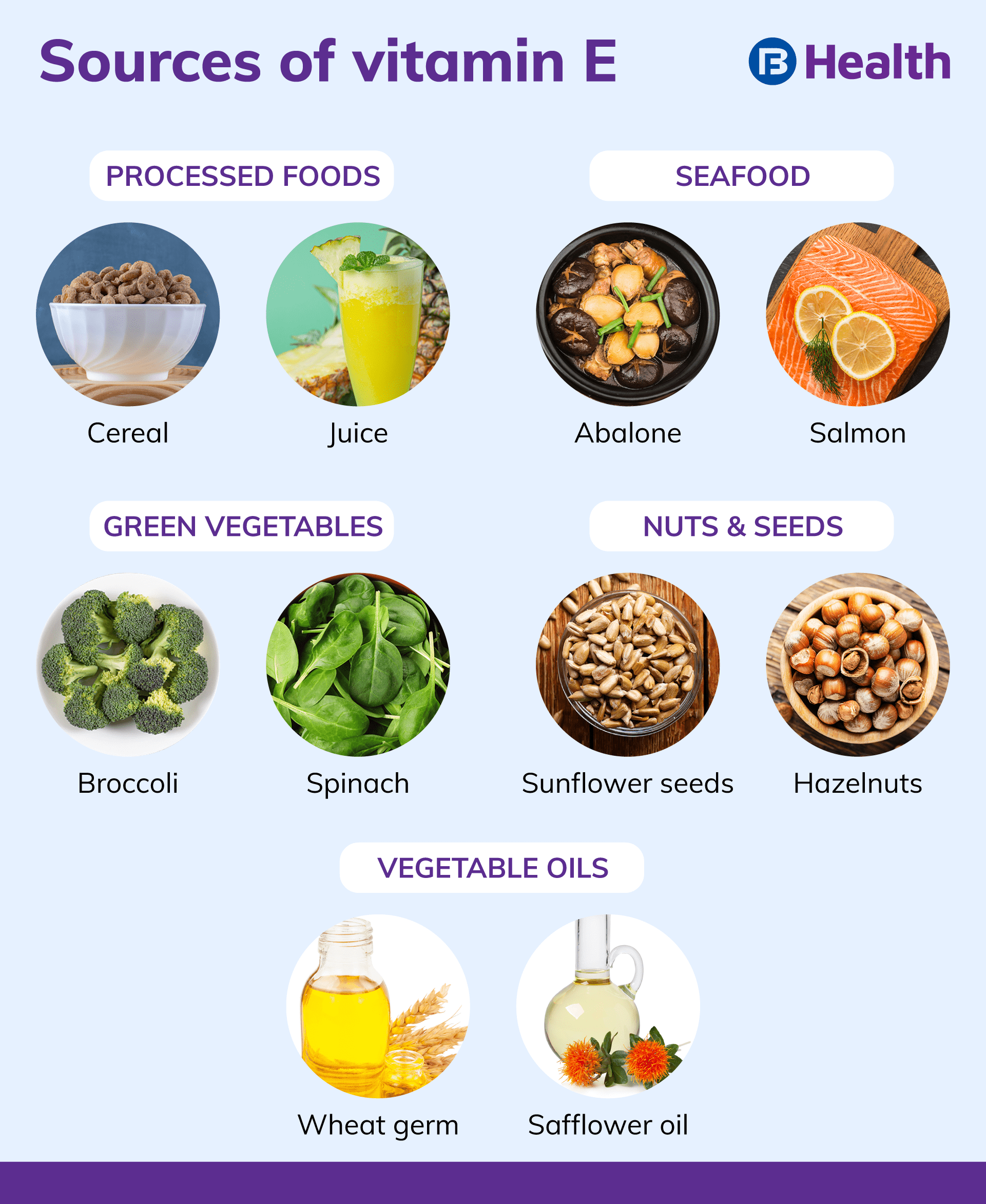
Vitamin E Foods Functions How Much Do You Need More Eufic Vitamin e has a protective effect on the cells in your eyes. getting enough of this nutrient could lower your risk of age related macular degeneration (amd) and cataracts. “just like the rest of. Grants and funding. vitamin e is a fat soluble antioxidant that can protect the polyunsaturated fatty acids (pufas) in the membrane from oxidation, regulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ros) and reactive nitrogen species (rns), and modulate signal transduction. immunomodulatory effects of vitamin e have b …. Vitamin e is a fat soluble antioxidant that can protect the polyunsaturated fatty acids (pufas) in the membrane from oxidation, regulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ros) and reactive nitrogen species (rns), and modulate signal transduction. immunomodulatory effects of vitamin e have been observed in animal and human models under normal and disease conditions. with advances in. Supporting proper immune function. promoting cellular signaling and metabolic processes. vitamin e exists naturally in certain foods, including: seeds. nuts. some vegetables. some fortified.

10 Useful Health Benefits Of Vitamin E You Must To Know My Health Only Vitamin e is a fat soluble antioxidant that can protect the polyunsaturated fatty acids (pufas) in the membrane from oxidation, regulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ros) and reactive nitrogen species (rns), and modulate signal transduction. immunomodulatory effects of vitamin e have been observed in animal and human models under normal and disease conditions. with advances in. Supporting proper immune function. promoting cellular signaling and metabolic processes. vitamin e exists naturally in certain foods, including: seeds. nuts. some vegetables. some fortified. A primary barrier to characterizing the roles of vitamin e in health is the lack of validated biomarkers for vitamin e intake and status to help relate intakes to valid predictors of clinical outcomes . this section focuses on four diseases and disorders in which vitamin e might be involved: heart disease, cancer, eye disorders, and cognitive. It found that men assigned to take daily vitamin e supplements had a 32% lower risk of developing prostate cancer—and a 41% lower risk of dying from prostate cancer—than men given a placebo. vitamin e’s protective effect was strongest for men whose cancers were far enough along that they could be detected by a clinical exam.

12 Best Food Sources Of Vitamin E This Infographic Shows 12 Foods That Are High In Vitamin E A primary barrier to characterizing the roles of vitamin e in health is the lack of validated biomarkers for vitamin e intake and status to help relate intakes to valid predictors of clinical outcomes . this section focuses on four diseases and disorders in which vitamin e might be involved: heart disease, cancer, eye disorders, and cognitive. It found that men assigned to take daily vitamin e supplements had a 32% lower risk of developing prostate cancer—and a 41% lower risk of dying from prostate cancer—than men given a placebo. vitamin e’s protective effect was strongest for men whose cancers were far enough along that they could be detected by a clinical exam.

Comments are closed.