Tropical Rainforest Consumers
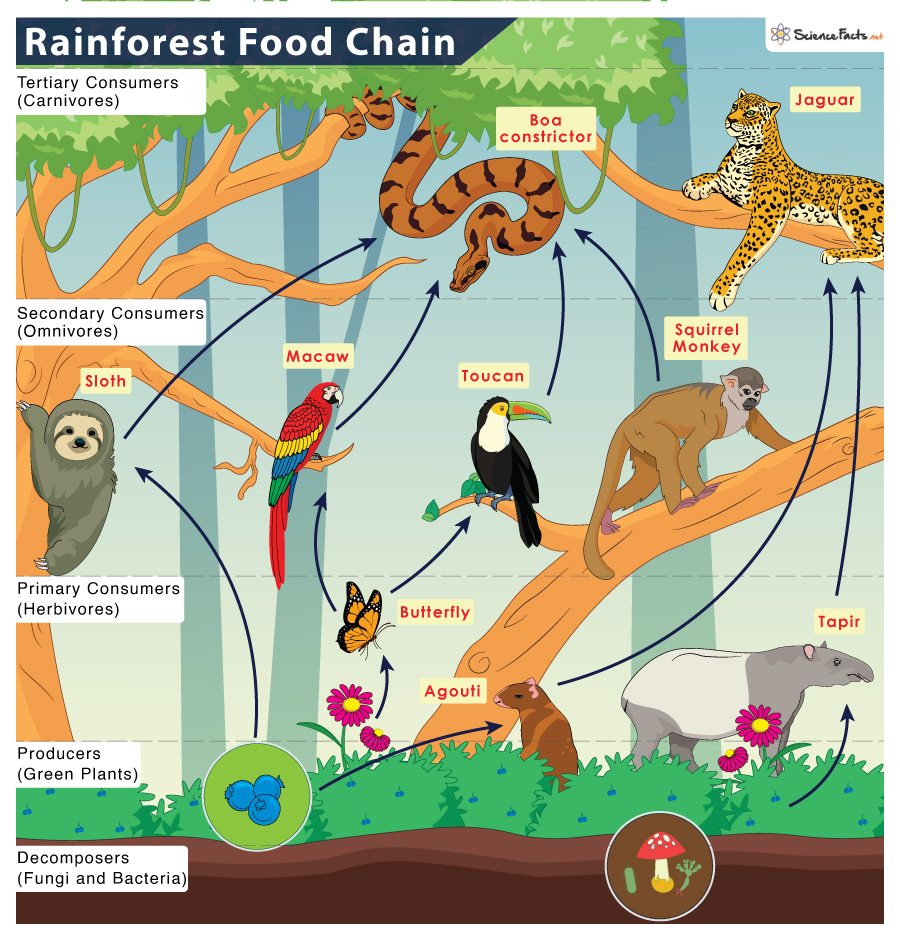
Tropical Rainforest Food Chain Examples And Diagram Learn how energy flows through the rainforest ecosystem when predators eat their prey. find out the five groups of organisms in the food chain, from producers to decomposers, and see examples of each group. The competitive world of the tropical rainforest food chain includes different levels of animal consumers, such as monkeys, ocelots and birds of prey. at the top of the food chain sit the apex predators like jaguars, crocodiles and the green anaconda, one of the largest snakes in the world.

Amazon Rainforest Animals Tropical Rainforest Food Web In the rainforest, these secondary consumers help control the number of herbivores, which keeps the whole ecosystem in balance. this way, no single animal or plant grows out of control, and all living things get what they need to survive. predators of the rainforest. snakes. snakes are common secondary consumers in the rainforest. In the vibrant tropical rainforest, primary consumers are key to the food chain. they include sloths, monkeys, and many insects. these herbivores feed on the lush plants, turning their energy into a form for higher levels in the food web. diverse herbivore species. the tropical rainforest is full of different herbivores, each fitting into its. The primary producers are at the foundation of the rainforest’s ecological system — the sun and the trees. ranging from the oldest largest species to shrubs, trees play an integral part in the rainforest food chain and web. they harness sunlight through the process of photosynthesis, and they are the main architects of the rainforest. Tropical rainforest secondary consumers are organisms who eat the primary consumers of the rainforest. they are generally carnivores as they eat other animals. among the secondary consumers of the.

Comments are closed.