Trophic Levels Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer Decomposers

Trophic Levels Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer Decomposers Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. Secondary consumers eat herbivores. they are at the third trophic level. in a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. in the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. they are at the fourth trophic level.
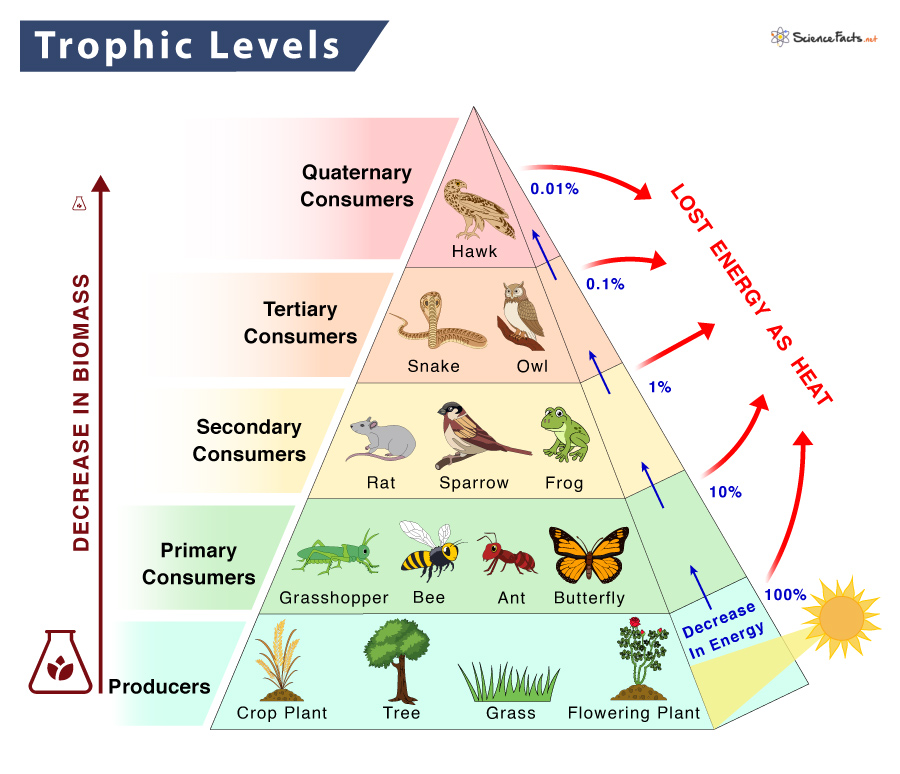
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 19.1.1). figure 19.1.1: example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Trophic level three consists mostly of omnivores that feed on producers and primary consumers and are secondary consumers. fourth trophic level: tertiary consumers . next to the secondary consumers at the fourth trophic level are the tertiary consumers, primarily carnivores, which prey on secondary consumers. carnivorous animals like foxes. The second trophic level consists of herbivores, these organisms gain energy by eating primary producers and are called primary consumers. trophic levels three, four and five consist of carnivores and omnivores. carnivores are animals that survive only by eating other animals, whereas omnivores eat animals and plant material. The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the.
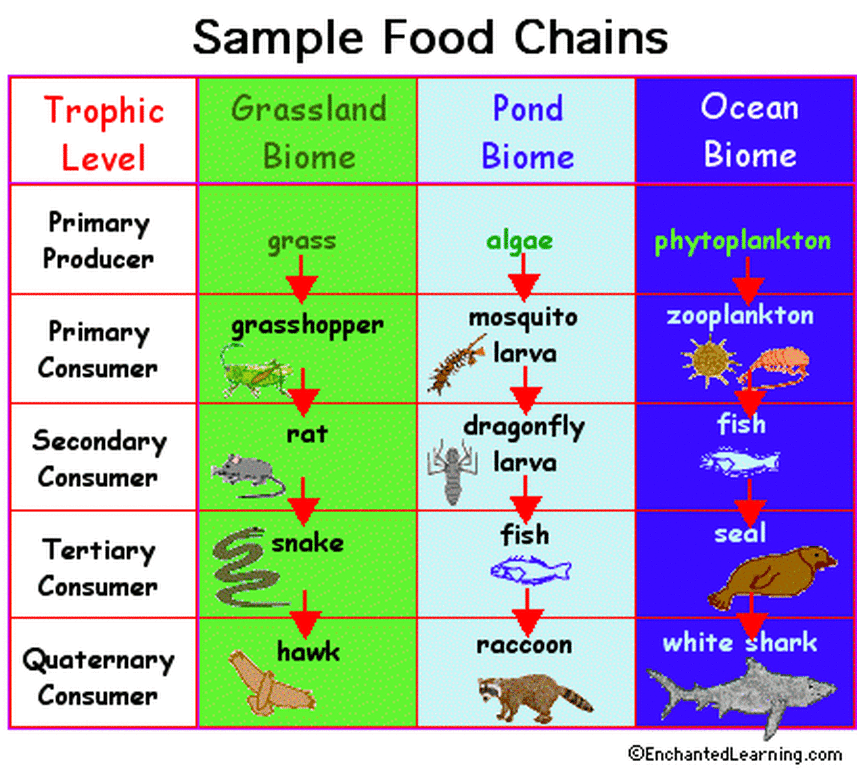
Food Chain And Web Ecology The second trophic level consists of herbivores, these organisms gain energy by eating primary producers and are called primary consumers. trophic levels three, four and five consist of carnivores and omnivores. carnivores are animals that survive only by eating other animals, whereas omnivores eat animals and plant material. The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the. The second trophic level in all food chains is an herbivore or omnivore close omnivore an animal that eats both plants and meat. called a primary consumer. either secondary or tertiary. A trophic level refers to a level or a position in a food chain, a food web, or an ecological pyramid. it is occupied by a group of organisms that have a similar feeding mode. in an ecological pyramid, the various trophic levels are primary producers (at the base), consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.), and predators (apex).

Trophic Level Definition Examples Facts Britannica The second trophic level in all food chains is an herbivore or omnivore close omnivore an animal that eats both plants and meat. called a primary consumer. either secondary or tertiary. A trophic level refers to a level or a position in a food chain, a food web, or an ecological pyramid. it is occupied by a group of organisms that have a similar feeding mode. in an ecological pyramid, the various trophic levels are primary producers (at the base), consumers (primary, secondary, tertiary, etc.), and predators (apex).

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary

Comments are closed.