Sleep Apnea In Children

Pediatric Sleep Apnea Ultimate Guide For Infants Babies And Children Sleep Advisor Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea is a sleep disorder in which your child's breathing is partially or completely blocked during sleep. it can happen several times a night. the condition occurs when the upper airway narrows or is blocked during sleep. there are differences between pediatric obstructive sleep apnea and adult sleep apnea. Up to date. sleep apnea is a condition in which breathing is interrupted during sleep. these pauses in breathing affect sleep quality and can lead to daytime sleepiness and behavior issues in children. the two types of sleep apnea are obstructive sleep apnea (osa) and central sleep apnea (csa). in osa, a person tries to breathe but is unable to.
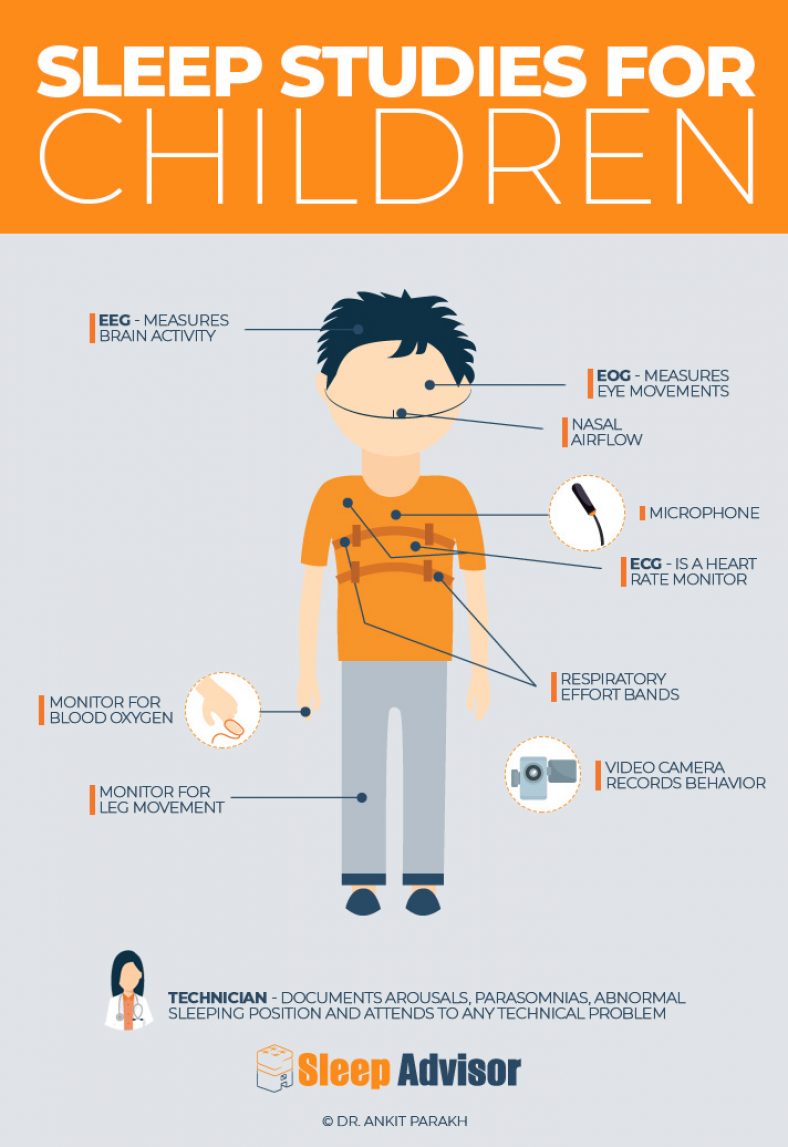
Sleep Apnea In Children Signs Symptoms And Treatments Pediatric sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that causes children to have pauses in their breathing while they sleep. two types of sleep apnea affect children: obstructive sleep apnea and central. The main test to check for sleep apnea in children is called a polysomnogram. this involves an overnight sleep test. sensors are placed on your child's body. the sensors record brain waves, breathing patterns, snoring, oxygen levels, heart rate and muscle activity while your child sleeps. this test may take place at a sleep center. Obstructive sleep apnea is when a child briefly stops breathing while sleeping. it happens because of a blockage in the upper airway. this is the passages through the nose and mouth to the windpipe and lungs. the pause in breathing may occur many times in a night, disrupting the child’s sleep. most children will snore, but other symptoms. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (osa) is a childhood disorder in which there is upper airway dysfunction causing complete or partial airway obstruction during sleep leading to decreased oxygen saturation or arousals from sleep. it can have dramatic effects on childhood behavior, neurodevelopment, metabolism, and overall health. early recognition, evaluation, and treatment are important to.
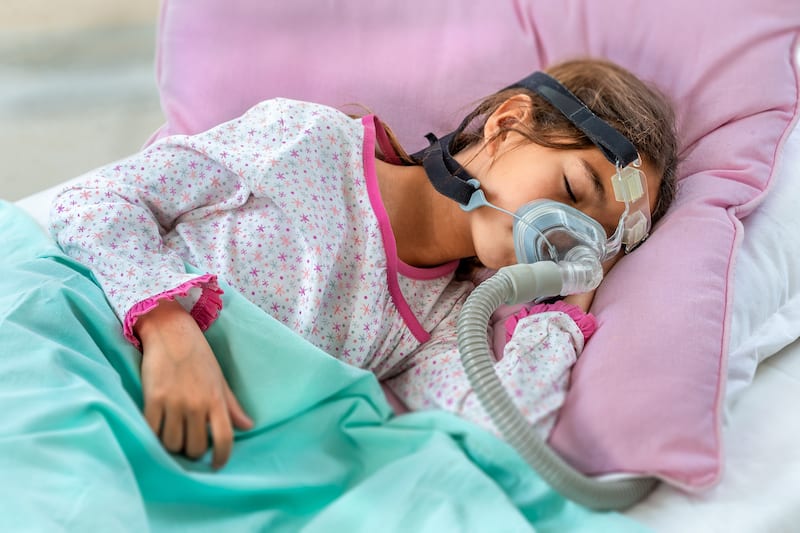
Children And Sleep Apnea Sleep Foundation Obstructive sleep apnea is when a child briefly stops breathing while sleeping. it happens because of a blockage in the upper airway. this is the passages through the nose and mouth to the windpipe and lungs. the pause in breathing may occur many times in a night, disrupting the child’s sleep. most children will snore, but other symptoms. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (osa) is a childhood disorder in which there is upper airway dysfunction causing complete or partial airway obstruction during sleep leading to decreased oxygen saturation or arousals from sleep. it can have dramatic effects on childhood behavior, neurodevelopment, metabolism, and overall health. early recognition, evaluation, and treatment are important to. “obstructive sleep apnea affects 3 to 6 percent of children and is associated with repetitive narrowing of the airways, which is the breathing tube from the mouth and the nose down to the lungs,” explains yale medicine's craig a. canapari, md, director of the pediatric sleep medicine program. “this can happen multiple times in the night. Sleep apnea is very common. around the world, an estimated 1 billion people have sleep apnea. among children, obstructive sleep apnea occurs in up to 1% to 5% of all ages including babies, infants, toddlers, children, adolescents and teenagers. childhood obstructive sleep apnea is most common between the ages of 2 and 6 years old.
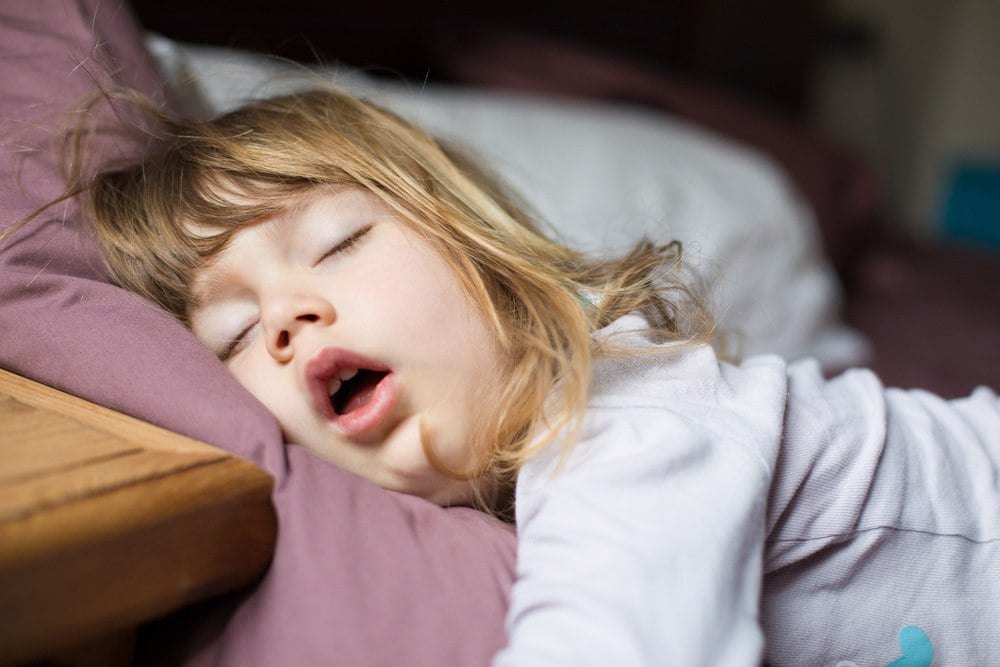

Sleep Apnea In Children Signs Symptoms And Causes “obstructive sleep apnea affects 3 to 6 percent of children and is associated with repetitive narrowing of the airways, which is the breathing tube from the mouth and the nose down to the lungs,” explains yale medicine's craig a. canapari, md, director of the pediatric sleep medicine program. “this can happen multiple times in the night. Sleep apnea is very common. around the world, an estimated 1 billion people have sleep apnea. among children, obstructive sleep apnea occurs in up to 1% to 5% of all ages including babies, infants, toddlers, children, adolescents and teenagers. childhood obstructive sleep apnea is most common between the ages of 2 and 6 years old.

Comments are closed.