Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction Structure And Functions
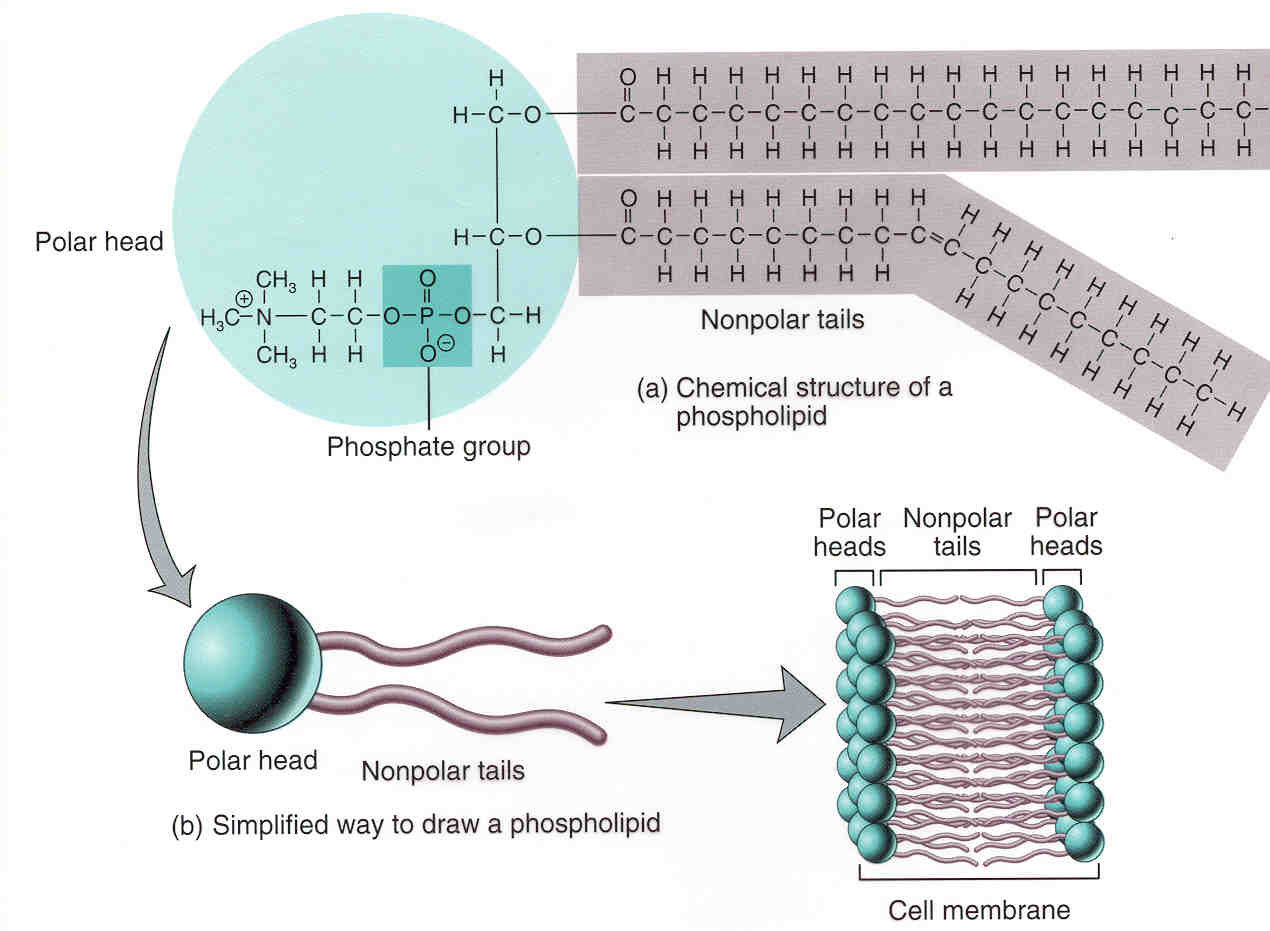
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction Structure And Functions Fluid mosaic model (source: link) as its name implies, the phospholipid bilayer is made up of many phospholipids that lined up altogether. as shown in the diagram above, the bilayer is composed of hydrophilic (water loving) heads that interact with the water on the outside environment, and a hydrophobic (water fearing) tails that face each other in the inner structure of the membrane. The phospholipid bilayer consists of phospholipids arranged in two layers with exterior facing hydrophilic polar heads and interior hydrophobic non polar tails. this imparts the amphiphilic nature to phospholipids. structurally, a phospholipid molecule comprises two fatty acid tails and a head with glycerol (3 carbon alcohol) and a phosphate.
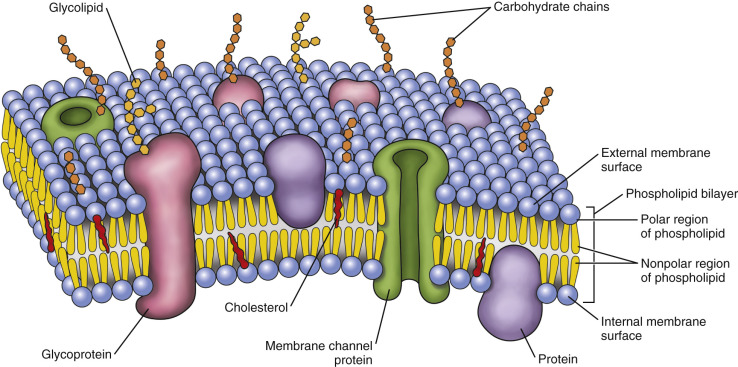
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction Structure And Functions Phospholipid definition. phospholipid bilayer is basically a special form of lipid molecule which is mainly the major constituent of the cell membrane. fats, waxes, and vitamins are the molecules that are lipids in nature and composed of lipids. while phospholipid is comprised of two molecules of fatty acids, phosphate group, and a glycerol. A phospholipid bilayer. the plasma membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fatty acids and alcohol. the phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called aphospholipid bilayer. as shown in figure below, each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The structure and function of the plasma membrane is consistent amongst all forms of life. the plasma membrane serves to separate the interior environment of the cell from the exterior and consists of a double layer of lipids called the phospholipid bilayer. in this unit, we will explore the structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. these membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells . the cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus , and.
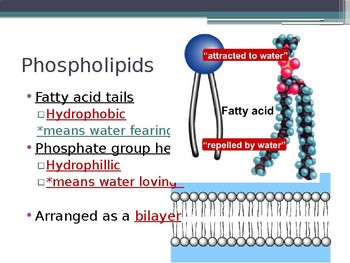
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction Structure And Functions The structure and function of the plasma membrane is consistent amongst all forms of life. the plasma membrane serves to separate the interior environment of the cell from the exterior and consists of a double layer of lipids called the phospholipid bilayer. in this unit, we will explore the structure and function of the phospholipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. these membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells . the cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus , and. The phospholipid bilayer plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and stability of cells. it acts as a semi permeable barrier, allowing small, hydrophobic molecules to pass through while excluding larger, hydrophilic molecules. this allows cells to regulate what enters and exits the cell and helps to maintain the proper balance of ions. 1 introduction. the phospholipid bilayer plasma membrane is not simply a passive selective permeability barrier between the inside and outside of the cell; it is an active participant in signal transduction. the phospholipid composition directly influences membrane morphology and physical properties.
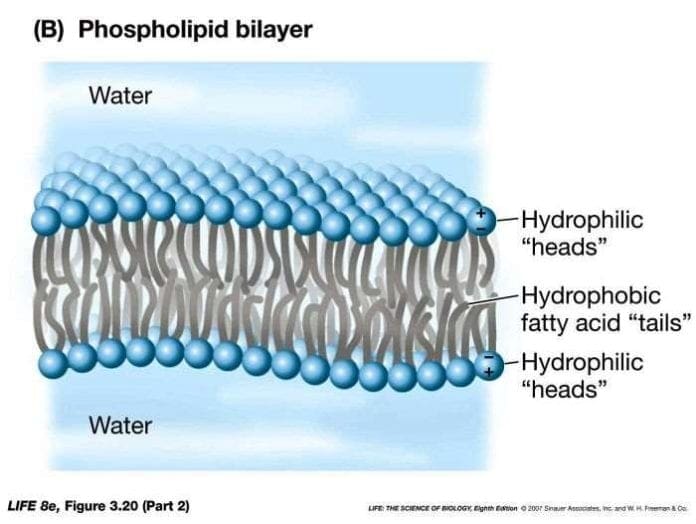
Phospholipid Bilayer Lipid Bilayer Structures Functions The phospholipid bilayer plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and stability of cells. it acts as a semi permeable barrier, allowing small, hydrophobic molecules to pass through while excluding larger, hydrophilic molecules. this allows cells to regulate what enters and exits the cell and helps to maintain the proper balance of ions. 1 introduction. the phospholipid bilayer plasma membrane is not simply a passive selective permeability barrier between the inside and outside of the cell; it is an active participant in signal transduction. the phospholipid composition directly influences membrane morphology and physical properties.

Comments are closed.