Kirchhoff S Laws Determine Vo In The Circuit In Fig Youtube

Kirchhoff S Laws Determine Vo In The Circuit In Fig Youtube Welcome to the electrical engineering channel! here you’ll find tutorials, lectures, and resources to help you excel in your studies and career. whether you'. Welcome to the electrical engineering channel! here you’ll find tutorials, lectures, and resources to help you excel in your studies and career. whether you'.

03 Determine Vo In The Circuit In Fig 2 80 Circuit Analysis Youtube Kirchhoff’s voltage law (kvl) is kirchhoff’s second law that deals with the conservation of energy around a closed circuit path. gustav kirchhoff’s voltage law is the second of his fundamental laws we can use for circuit analysis. his voltage law states that for a closed loop series path the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any. Kirchhoff’s law (kcl) and (kvl) example 11; determine the branch currents in the network of fig. below when the value of each branch resistance is one ohm. solution; let the current directions be as shown in fig. 2.14. apply kirchhoff’s voltage law to the closed circuit abda, we get. 5 – x – z y = 0 or x – y z = 5 … (i). Solved example on kcl and kvl (kirchhoff’s laws) example: resistors of r1= 10Ω, r2 = 4Ω and r3 = 8Ω are connected up to two batteries (of negligible resistance) as shown. find the current through each resistor. solution: assume currents to flow in directions indicated by arrows. apply kcl on junctions c and a. R. figure 5. simple resistive circuit. the i v curve for a resistor is a straight line (the current is directly proportional to the voltage). the slope of the straight line is 1 (see figure 6) for convenience we define the. r. conductance (g) of a circuit element as the inverse of the resistance. = v = gv.

Determine Vo T In The Circuit Of Fig Sinusoids And Phasors Youtube Solved example on kcl and kvl (kirchhoff’s laws) example: resistors of r1= 10Ω, r2 = 4Ω and r3 = 8Ω are connected up to two batteries (of negligible resistance) as shown. find the current through each resistor. solution: assume currents to flow in directions indicated by arrows. apply kcl on junctions c and a. R. figure 5. simple resistive circuit. the i v curve for a resistor is a straight line (the current is directly proportional to the voltage). the slope of the straight line is 1 (see figure 6) for convenience we define the. r. conductance (g) of a circuit element as the inverse of the resistance. = v = gv. This video demonstrates how to obtain the differential function that describes current in an electrical circuit over time. this includes using kirchhoff's vo. Kirchhoff’s current law states that the total current entering a junction (or node) in a circuit is equal to the total current leaving the junction. in simpler terms, kcl is the total current flowing into a node must equal the total current flowing out of it. kcl mathematical expression: Σ i in = Σ i out. 2.
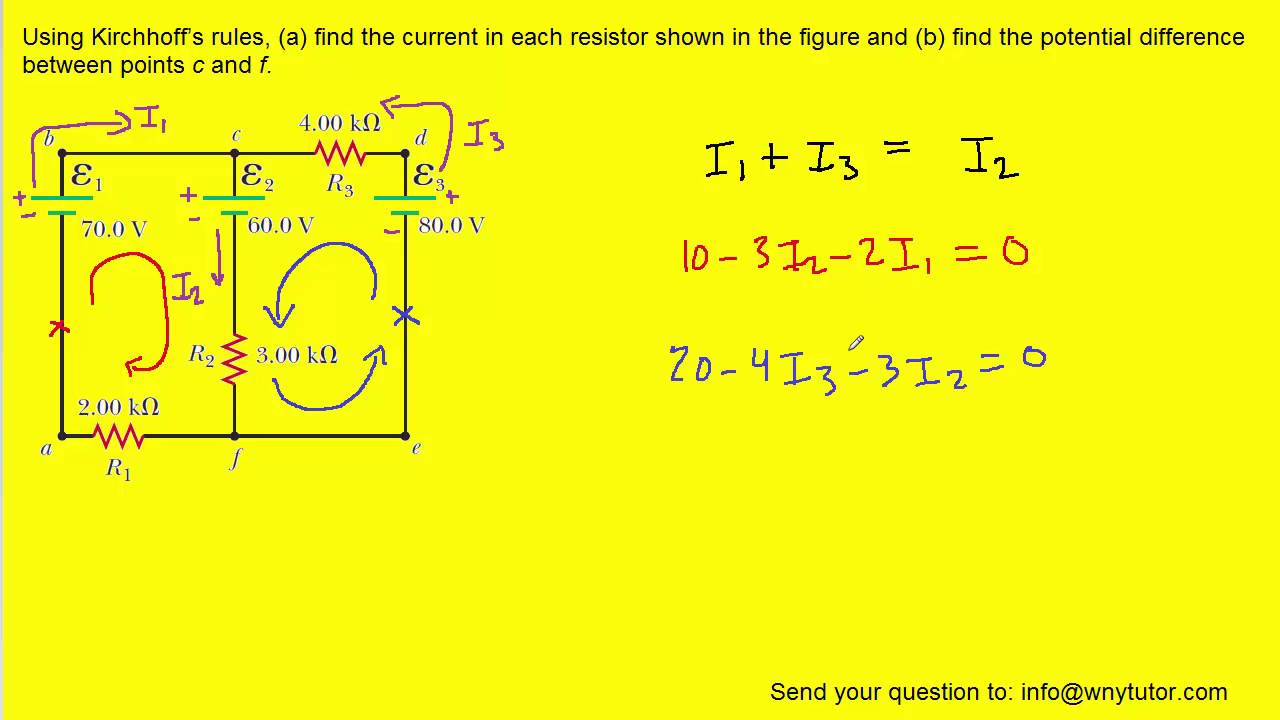
Using Kirchhoff S Rules Find The Current In Each Resistor Shown In Figure Youtube This video demonstrates how to obtain the differential function that describes current in an electrical circuit over time. this includes using kirchhoff's vo. Kirchhoff’s current law states that the total current entering a junction (or node) in a circuit is equal to the total current leaving the junction. in simpler terms, kcl is the total current flowing into a node must equal the total current flowing out of it. kcl mathematical expression: Σ i in = Σ i out. 2.

Kirchoff S Law Circuits Tutorial Harder Example Youtube

Comments are closed.