Find Out What Happens To Medical Waste Once It Leaves Hospitals

Find Out What Happens To Medical Waste Once It Leaves Hospitals Youtube What happens to medical waste once it leaves the hospital? some people think the lifespan of medical equipment ends once it hits the trash. but i found out there's a whole process that happens after. This type of waste was once collected in special bags and plastic boxes in clinical settings and then disposed of like normal trash. however, this process was quickly found to spread diseases and viruses and potentially cause outbreaks. today, the red biohazardous containers and bags seen throughout hospitals and doctors’ offices are used to.

What Happens To Medical Waste After Leaving Medical Facilities The covid 19 pandemic is causing an increase of medical waste in parts of the world. china not only had to build more hospitals to accommodate a surge of pat. Medical waste must be collected by a licensed medical waste hauler, as this waste disposal is closely monitored and regulated in most states. the waste must be treated and rendered harmless before it can be recycled or thrown away. let medxwaste take care of your disposal to mitigate risk, maintain compliance, and keep communities safe. Stage five: sending treated waste to its final destination. after medical waste has been rendered non infectious or destroyed, it is sent to a landfill or a waste to energy facility (wte), depending on local regulations. any waste sent to a wte site is converted to usable, clean electricity. the wte process employs specially designed boilers. The waste is carried in sealed medical bags that are tied shut inside sealed medical containers. the waste is placed into a cart and dumped into what’s called a hopper. “steam is injected and then it moves under microwaves which also provide more heat,” fitzpatrick said. “we heat the waste up to over 200 degrees fahrenheit.

Medical Waste Disposal Definitive Guide Updated 2023 Stage five: sending treated waste to its final destination. after medical waste has been rendered non infectious or destroyed, it is sent to a landfill or a waste to energy facility (wte), depending on local regulations. any waste sent to a wte site is converted to usable, clean electricity. the wte process employs specially designed boilers. The waste is carried in sealed medical bags that are tied shut inside sealed medical containers. the waste is placed into a cart and dumped into what’s called a hopper. “steam is injected and then it moves under microwaves which also provide more heat,” fitzpatrick said. “we heat the waste up to over 200 degrees fahrenheit. Medical waste. medical waste is a subset of wastes generated at health care facilities, such as hospitals, physicians' offices, dental practices, blood banks, and veterinary hospitals clinics, as well as medical research facilities and laboratories. generally, medical waste is healthcare waste that that may be contaminated by blood, body fluids. There are two primary methods for treating regulated medical waste: autoclaving—this is where waste is subjected to a timed, high temperature, pressured steaming process to render any infectious agents neutral. the waste is then suitable for being taken to a landfill. in general, items like sharps and bio contaminated materials are autoclaved.
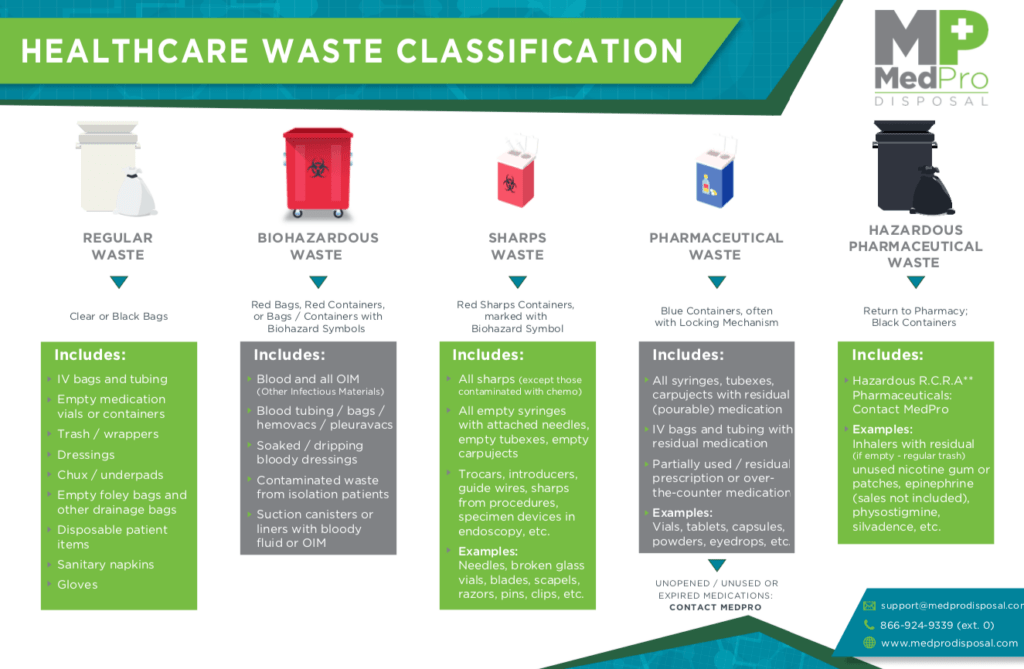
What Is Medical Waste Learn More With Medpro Disposal Medical waste. medical waste is a subset of wastes generated at health care facilities, such as hospitals, physicians' offices, dental practices, blood banks, and veterinary hospitals clinics, as well as medical research facilities and laboratories. generally, medical waste is healthcare waste that that may be contaminated by blood, body fluids. There are two primary methods for treating regulated medical waste: autoclaving—this is where waste is subjected to a timed, high temperature, pressured steaming process to render any infectious agents neutral. the waste is then suitable for being taken to a landfill. in general, items like sharps and bio contaminated materials are autoclaved.

Comments are closed.