Do Women Work Longer Hours Than Men World Economic Forum

Do Women Work Longer Hours Than Men World Economic Forum Nov 2, 2015. when all work – paid and unpaid – is accounted for, women work longer hours than men. this is according to the un’s the world’s women 2015 report, which found women spend an average of 30 minutes a day longer than men on paid and unpaid work in developed countries and 50 minutes longer in developing countries. The advancement of women at work is good for everyone – potentially increasing global gdp by 20%, according to the world bank. the world economic forum’s global gender gap report 2024 shows progress for women has slowed overall, but employment rates are up. the economic participation and opportunity gap has closed by 17 years since the last.
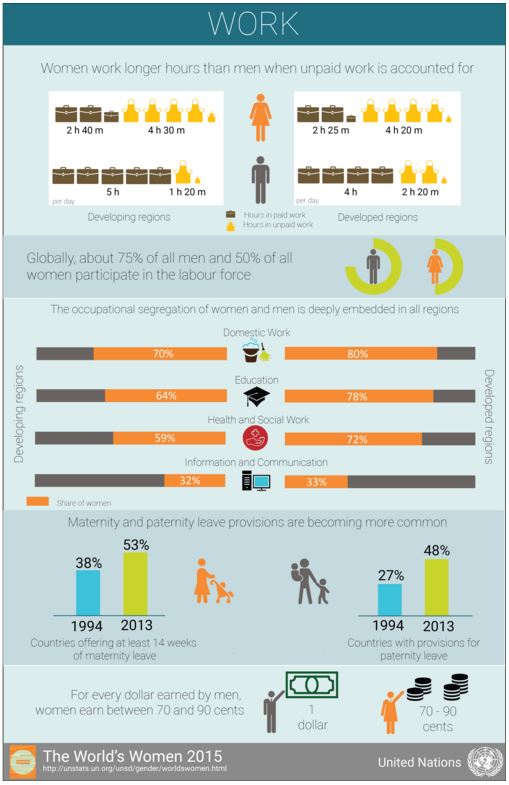
Do Women Work Longer Hours Than Men World Economic Forum Between 2019 and 2020, the global women’s labour force participation rate declined by 3.4%, as compared to 2.4% for men. 5 women have been (re )entering the workforce at a slightly higher rate than men since then, resulting in a modest recovery in gender parity. between the 2022 and 2023 editions, parity in the labour force participation rate. Bbc news. women work on average 39 more days a year than men according to the world economic forum. women work on average 50 minutes more a day than men, data from the wef's global gender gap. The gender pay gap (or the gender wage gap) is a metric that tells us the difference in pay (or wages, or income) between women and men. it's a measure of inequality and captures a concept that is broader than the concept of equal pay for equal work. differences in pay between men and women capture differences along many possible dimensions. Across all world regions, women spend more time on unpaid care work than men. on average, women spend between three and six hours on unpaid care work per day, while men spend between half an hour and two hours. if we consider the sum of paid and unpaid work, women tend to work more than men – on average, 2.6 extra hours per week across the oecd.

Do Women Work Longer Hours Than Men World Economic Forum The gender pay gap (or the gender wage gap) is a metric that tells us the difference in pay (or wages, or income) between women and men. it's a measure of inequality and captures a concept that is broader than the concept of equal pay for equal work. differences in pay between men and women capture differences along many possible dimensions. Across all world regions, women spend more time on unpaid care work than men. on average, women spend between three and six hours on unpaid care work per day, while men spend between half an hour and two hours. if we consider the sum of paid and unpaid work, women tend to work more than men – on average, 2.6 extra hours per week across the oecd. In terms of total work, women work longer hours than men in china, korea, and taiwan (the gaps are 42.5, 45.7, and 60.5 minutes per day, respectively). due to long paid work hours of men in japan, japanese men have longer total work time than women (the gap is 15.2 minutes per day). However, men get paid for 10 more of their weekly hours than women do. since the 1970s, women have increased their paid working hours by more than five hours to 22 per week, and have cut unpaid.

It S Official Women Work Nearly An Hour Longer Than Men Every Day World Economic Forum In terms of total work, women work longer hours than men in china, korea, and taiwan (the gaps are 42.5, 45.7, and 60.5 minutes per day, respectively). due to long paid work hours of men in japan, japanese men have longer total work time than women (the gap is 15.2 minutes per day). However, men get paid for 10 more of their weekly hours than women do. since the 1970s, women have increased their paid working hours by more than five hours to 22 per week, and have cut unpaid.

It S Official Women Work Nearly An Hour Longer Than Men Every Day World Economic Forum

Comments are closed.