Differential Equations 20 Characteristic Equation 2nd Order

Differential Equations 20 Characteristic Equation 2nd Order Youtube Definition: characteristic equation. the characteristic equation of the second order differential equation ay'' by' cy=0 is. a\lambda^2 b\lambda c=0. \nonumber. the characteristic equation is very important in finding solutions to differential equations of this form. To solve a linear second order differential equation of the form. d 2 ydx 2 p dydx qy = 0. where p and q are constants, we must find the roots of the characteristic equation. r 2 pr q = 0. there are three cases, depending on the discriminant p 2 4q. when it is. positive we get two real roots, and the solution is. y = ae r 1 x be r 2 x.

2nd Order Differential Equations Teaching Resources Solving linear 2nd order homogeneous with constant coefficients equation with the characteristic polynomial!. 3. second order differential equations. we now turn to second order differential equations. such equations involve the second derivative, y00(x). let’s assume that we can write the equation as y00(x) = f(x,y(x),y0(x)). we would like to solve this equation using simulink. this is accomplished using two integrators in order to output y0(x) and. Repeated roots – in this section we discuss the solution to homogeneous, linear, second order differential equations, ay′′ by′ cy = 0 a y ″ b y ′ c y = 0, in which the roots of the characteristic polynomial, ar2 br c = 0 a r 2 b r c = 0, are repeated, i.e. double, roots. we will use reduction of order to derive the second. Section 3.1 : basic concepts. in this chapter we will be looking exclusively at linear second order differential equations. the most general linear second order differential equation is in the form. p(t)y′′ q(t)y′ r(t)y = g(t) (1) (1) p (t) y ″ q (t) y ′ r (t) y = g (t) in fact, we will rarely look at non constant coefficient.
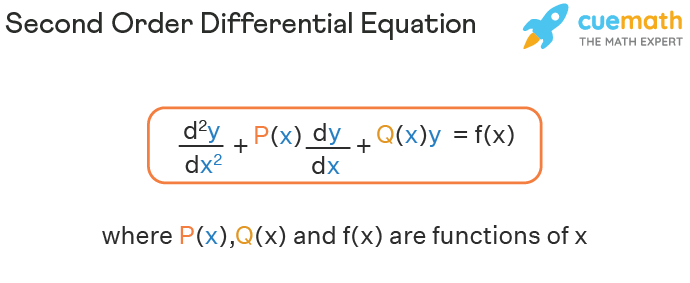
Second Order Differential Equation Solver Types Examples Methods Repeated roots – in this section we discuss the solution to homogeneous, linear, second order differential equations, ay′′ by′ cy = 0 a y ″ b y ′ c y = 0, in which the roots of the characteristic polynomial, ar2 br c = 0 a r 2 b r c = 0, are repeated, i.e. double, roots. we will use reduction of order to derive the second. Section 3.1 : basic concepts. in this chapter we will be looking exclusively at linear second order differential equations. the most general linear second order differential equation is in the form. p(t)y′′ q(t)y′ r(t)y = g(t) (1) (1) p (t) y ″ q (t) y ′ r (t) y = g (t) in fact, we will rarely look at non constant coefficient. Second order ordinary differential equations cheatsheet resolution based on the types of solution of the characteristic equation $\boxed{a\lambda^2 b\lambda c=0. This guess into (2.10) leads to the characteristic equation ar2 br c = 0.(2.11) the characteristic equation for namely, we compute the derivatives of y(x) = e rx, to get y(x) = re , and ay00 by0 cy = 0 is ar2 br c = 0. solutions of this quadratic equation lead to solutions of the differential equation. y(x) = r2erx. inserting into (2.10.

Second Order Linear Differential Equations Youtube Second order ordinary differential equations cheatsheet resolution based on the types of solution of the characteristic equation $\boxed{a\lambda^2 b\lambda c=0. This guess into (2.10) leads to the characteristic equation ar2 br c = 0.(2.11) the characteristic equation for namely, we compute the derivatives of y(x) = e rx, to get y(x) = re , and ay00 by0 cy = 0 is ar2 br c = 0. solutions of this quadratic equation lead to solutions of the differential equation. y(x) = r2erx. inserting into (2.10.

Differential Equation 2nd Order 2 Of 54 The Characteristic Equation Youtube

Comments are closed.