Checks And Balances The Bill Of Rights 10 Amendments U S Constitution Freedoms Social
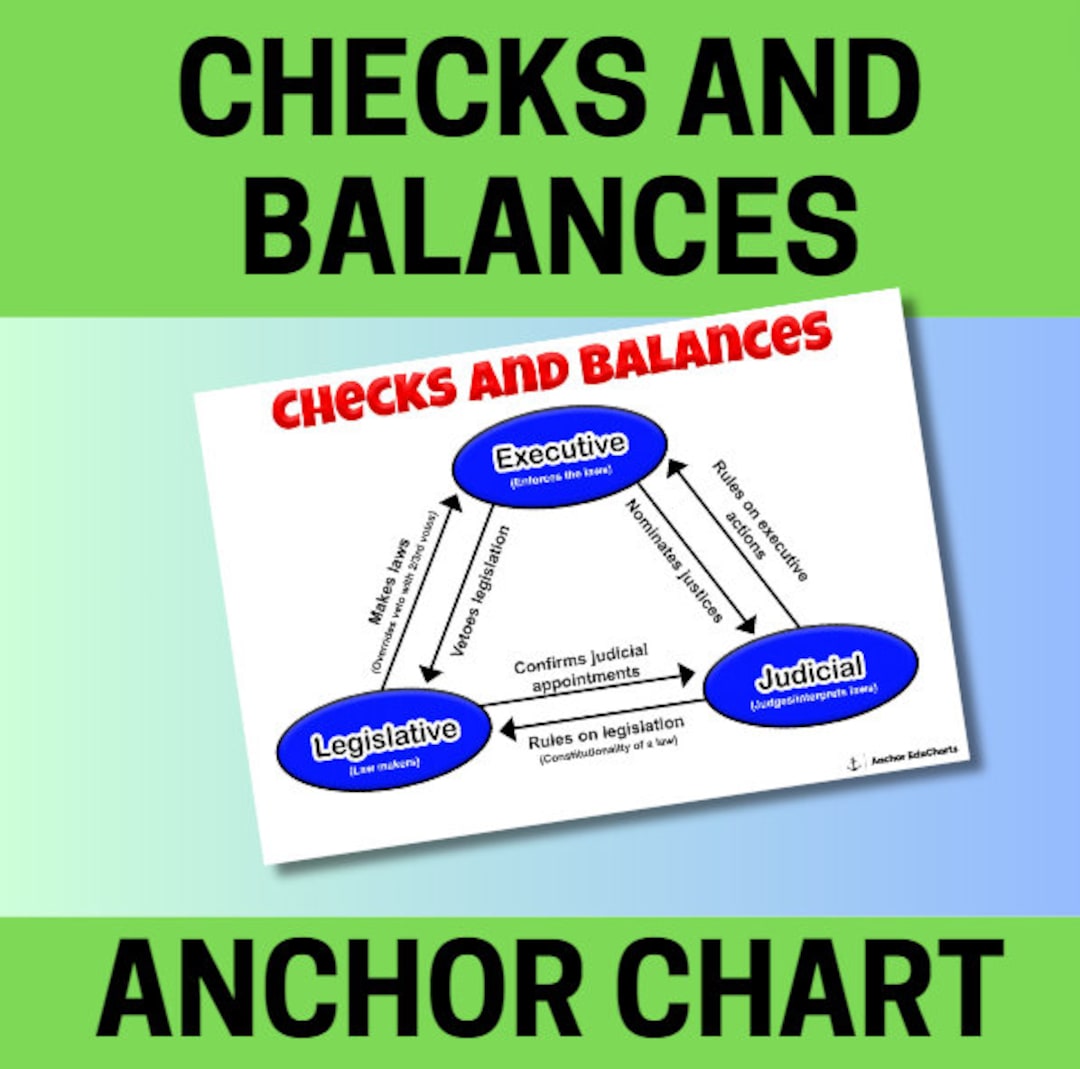
Checks And Balances The Bill Of Rights 10 Amendments U S Constitution Freedoms Social Separation of powers. the u.s. constitution establishes three branches of government: executive, legislative, and judicial. the president leads the executive branch, enforcing laws, commanding the military, and conducting foreign policy. the legislative branch, composed of the house of representatives and the senate, makes up congress. Print page. checks and balances refers to a system in u.s. government that ensures no one branch becomes too powerful. the framers of the u.s. constitution built a system that divides power.
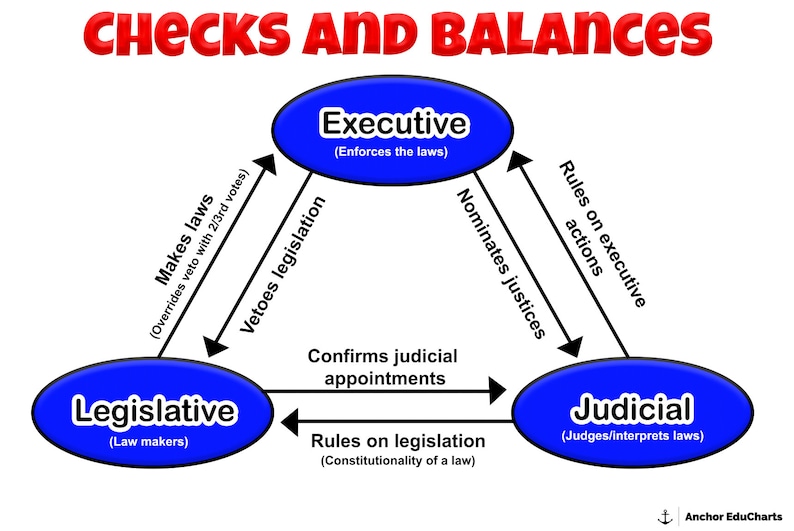
Checks And Balances The Bill Of Rights 10 Amendments U S Constitution Freedoms Social 1. marbury v. madison (1803) marbury v. madison (1803) significantly shaped american constitutional law. chief justice john marshall presided over the case, which established the supreme court's authority to review acts of congress and determine their constitutionality through judicial review. the case arose when william marbury petitioned for a writ of mandamus, compelling secretary of […]. Bill of rights. first amendment [religion, speech, press, assembly, petition (1791)] (see explanation) second amendment [right to bear arms (1791)] (see explanation) third amendment [quartering of troops (1791)] (see explanation) fourth amendment [search and seizure (1791)] (see explanation) fifth amendment [grand jury, double jeopardy, self. The bill of rights. the bill of rights is the first 10 amendments to the constitution. it spells out americans’ rights in relation to their government. it guarantees civil rights and liberties to the individual—like freedom of speech, press, and religion. it sets rules for due process of law and reserves all powers not delegated to the. Constitutional amendments reflecting checks and balances. after these four articles in the main text of the us constitution, a number of amendments in the 27 amendments ratified so far also touch on the separation of powers doctrine’s application in the checks and balances system of a tripartite federal government.

Bill Of Rights List Simple The bill of rights. the bill of rights is the first 10 amendments to the constitution. it spells out americans’ rights in relation to their government. it guarantees civil rights and liberties to the individual—like freedom of speech, press, and religion. it sets rules for due process of law and reserves all powers not delegated to the. Constitutional amendments reflecting checks and balances. after these four articles in the main text of the us constitution, a number of amendments in the 27 amendments ratified so far also touch on the separation of powers doctrine’s application in the checks and balances system of a tripartite federal government. The declaration stands on its own—it has never been amended—while the constitution has been amended 27 times. (the first ten amendments are called the bill of rights.) the declaration and bill of rights set limitations on government; the constitution was designed both to create an energetic government and also to constrain it. Bill of rights, in the united states, the first 10 amendments to the u.s. constitution, which were adopted as a single unit on december 15, 1791, and which constitute a collection of mutually reinforcing guarantees of individual rights and of limitations on federal and state governments. the bill of rights derives from the magna carta (1215.
What Section Is Checks And Balances In The Constitution The declaration stands on its own—it has never been amended—while the constitution has been amended 27 times. (the first ten amendments are called the bill of rights.) the declaration and bill of rights set limitations on government; the constitution was designed both to create an energetic government and also to constrain it. Bill of rights, in the united states, the first 10 amendments to the u.s. constitution, which were adopted as a single unit on december 15, 1791, and which constitute a collection of mutually reinforcing guarantees of individual rights and of limitations on federal and state governments. the bill of rights derives from the magna carta (1215.
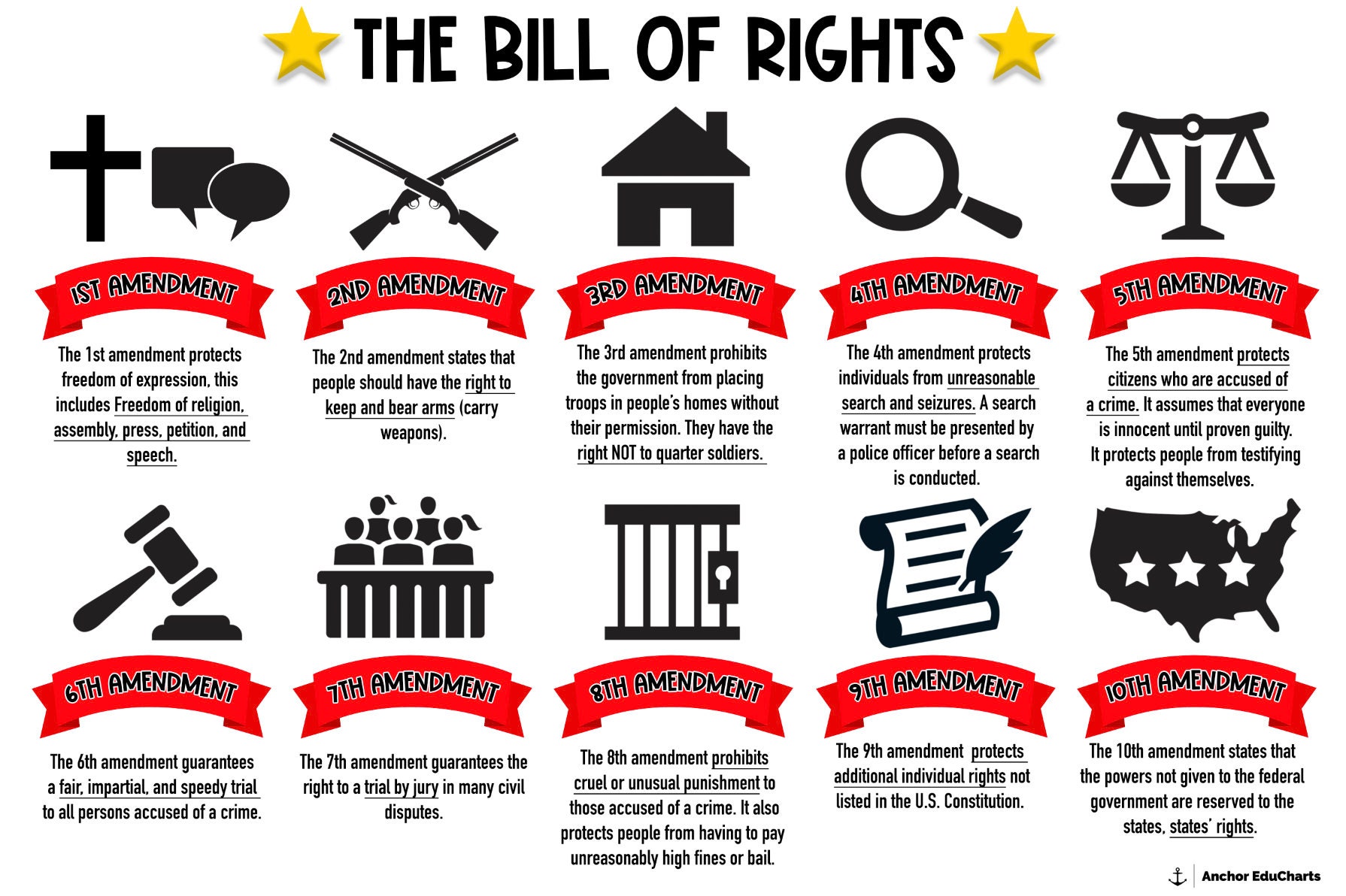
The Bill Of Rights 10 Amendments U S Constitution Freedoms Social Studies Anchor Charts

Comments are closed.