Annuity Ordinary And Annuity Due Present Future Value Financial Management Ch 3 Part

Annuity Ordinary And Annuity Due Present Future Value Financial Management Ch 3 Part Ch. 3: applying time value concepts. get a hint. annuity (ordinary annuity) a series of equal cash flow payments that are received or paid at equal intervals in time. 1 27. #ermi e learning #annuity #ordinaryannuitiy #annutiydue በዚህ ቻናል ሁሉም የአካውንቲን እና ፋይናስ ኮርሶች በጥሩ ሁኔታ ተዘጋጅተው ይቀርባሉ.

8 Of 26 Ch 6 Annuity Ordinary Vs Due Future Value Youtube #ermie learning #amortization #annuity በዚህ ቻናል ሁሉም የአካውንቲን እና ፋይናስ ኮርሶች በጥሩ ሁኔታ ተዘጋጅተው ይቀርባሉ 🛑🛑🛑. Ordinary annuities and annuities due differ in the timing of those recurring payments. the future value of an annuity is the total value of payments at a future point in time. the present value is. C = cash flows per period. i = interest rate. n = number of payments. let's look at an example of the present value of an annuity due. suppose you are a beneficiary designated to immediately. Fv 3 (annuity due) =5000 [ { (1 6%) 3 1 6%} x (1 6 %)]=16,873.08. note: the future value of an annuity due for rs. 5000 at 6 % for 3 years is higher than the fv of an ordinary annuity with the same amount, time, and rate of interest. this is due to the earlier payments made at the starting of the year, which provides an extra time period to.
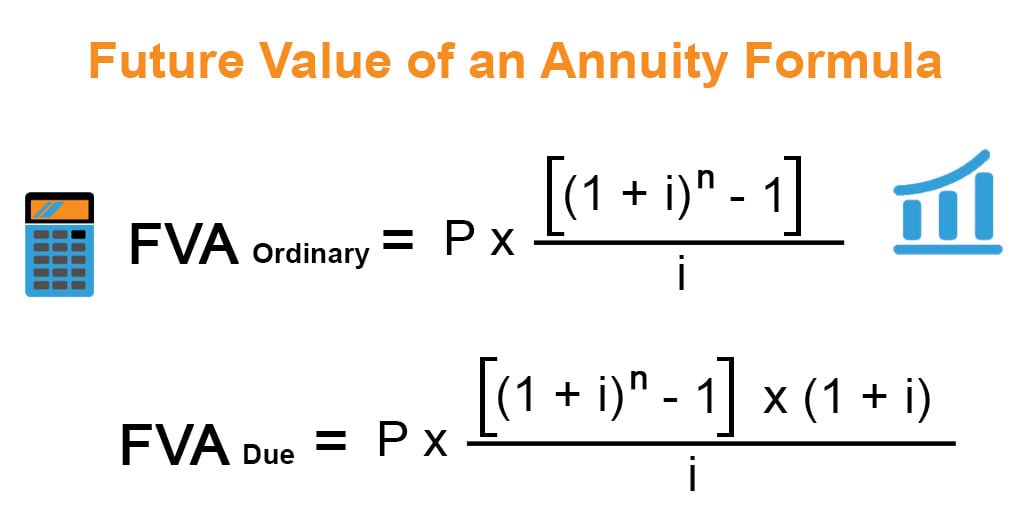
Future Value Of An Annuity Formula Example And Excel Template C = cash flows per period. i = interest rate. n = number of payments. let's look at an example of the present value of an annuity due. suppose you are a beneficiary designated to immediately. Fv 3 (annuity due) =5000 [ { (1 6%) 3 1 6%} x (1 6 %)]=16,873.08. note: the future value of an annuity due for rs. 5000 at 6 % for 3 years is higher than the fv of an ordinary annuity with the same amount, time, and rate of interest. this is due to the earlier payments made at the starting of the year, which provides an extra time period to. F v = p m t e r − 1 [e r t − 1] (1 (e r − 1) t) if type is ordinary annuity, t = 0 and we get the future value of an ordinary annuity with continuous compounding. f v = p m t e r − 1 [e r t − 1] otherwise type is annuity due, t = 1 and we get the future value of an annuity due with continuous compounding. f v = p m t e r − 1 [e r. An ordinary annuity will have a lower present value than an annuity due, all else being equal. present value of an annuity due example an investor with an ordinary annuity receives the payment at.
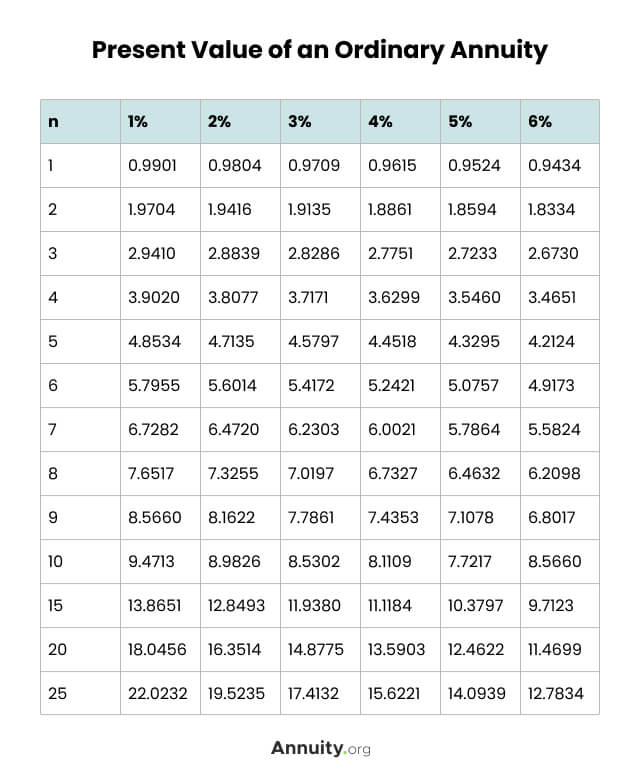
What Is An Annuity Table And How Do You Use One F v = p m t e r − 1 [e r t − 1] (1 (e r − 1) t) if type is ordinary annuity, t = 0 and we get the future value of an ordinary annuity with continuous compounding. f v = p m t e r − 1 [e r t − 1] otherwise type is annuity due, t = 1 and we get the future value of an annuity due with continuous compounding. f v = p m t e r − 1 [e r. An ordinary annuity will have a lower present value than an annuity due, all else being equal. present value of an annuity due example an investor with an ordinary annuity receives the payment at.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CalculatingPresentandFutureValueofAnnuities5-d76f3a6c09a54703afa365a16aff6607.png)
The Annuity Formula For The Present And Future Value Of Annuities

Comments are closed.