Annuity Formula Present Future Value Ordinary Due Annuities Efm
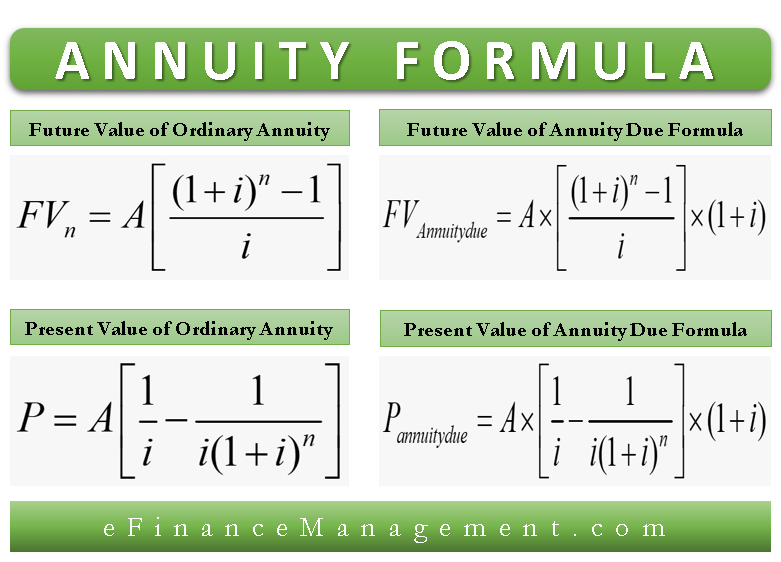
Annuity Formula Present Future Value Ordinary Due Annuities Efm Calculation using formula. fv 3 (annuity due) =5000 [ { (1 6%) 3 1 6%} x (1 6 %)]=16,873.08. note: the future value of an annuity due for rs. 5000 at 6 % for 3 years is higher than the fv of an ordinary annuity with the same amount, time, and rate of interest. this is due to the earlier payments made at the starting of the year, which provides. Ordinary annuities and annuities due differ in the timing of those recurring payments. the future value of an annuity is the total value of payments at a future point in time. the present value is.

Annuity Formula What Is Annuity Formula Examples Here’s the present value annuity formula: pmt x [ (1 – [1 (1 r)^n]) r] = the present value of the annuity. and here’s what each variable means: pmt: the amount the annuity pays you per period. r: the interest rate per period. n: the number of expected payment periods. Multiply this result by (1 i): 5.53 x (1 0.05) ≈ 5.8019. therefore, the future value of your annuity due with $1,000 annual payments at a 5 percent interest rate for five years would be. This refers to whether the annuity is an ordinary annuity that pays at the end of a period, such as the last day of the month, or annuity due that pays at the outset of a period, such as the first. F v = p m t e r − 1 [e r t − 1] (1 (e r − 1) t) if type is ordinary annuity, t = 0 and we get the future value of an ordinary annuity with continuous compounding. f v = p m t e r − 1 [e r t − 1] otherwise type is annuity due, t = 1 and we get the future value of an annuity due with continuous compounding. f v = p m t e r − 1 [e r.

Comments are closed.