Annuity Due Definition Calculation Formula And Examples 51 Off

Annuity Due Definition Calculation Formula And Examples 51 Off C = cash flows per period. i = interest rate. n = number of payments. let's look at an example of the present value of an annuity due. suppose you are a beneficiary designated to immediately. For calculation of the future value of an annuity, we can use the above formula: future value of annuity due = (1 5.00%) x 1000. future value of an annuity due will be . future value of an annuity=$ 5,801.91. therefore, the future value of the annual deposit of $1,000 will be $5,801.91.

Annuity Due Definition Formula Calculation With Examples The formula takes into account the payment amount, interest rate, and the time period over which the annuity will be paid. the formula to calculate the future value of an annuity due is: fv = p * [ (1 r) * ( (1 r)^n – 1) r] where: fv is the future value of the annuity due. p is the payment amount made at the beginning of each period. Example. an individual makes rental payments of $1,200 per month and wants to know the present value of their annual rentals over a 12 month period. the payments are made at the start of each month. the current interest rate is 8% per annum. using the formula above: fv of the investment = $1,200 x 11.57. Ordinary annuities and annuities due differ in the timing of those recurring payments. the future value of an annuity is the total value of payments at a future point in time. the present value is. For example, consider an annuity due with monthly payments of $1,000, an annual interest rate of 6%, and a duration of 5 years. first, convert the annual interest rate to a monthly rate (0.06 12 = 0.005). then, apply the modified formula: pv = $1,000 × [ (1 – (1 0.005)^ 60) 0.005] × (1 0.005). this calculation yields a present value.
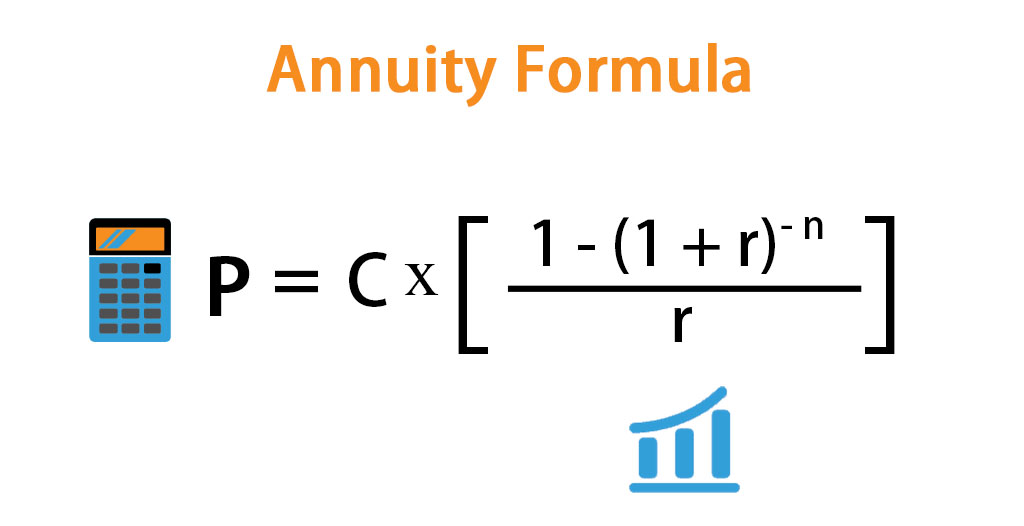
Annuity Formula Calculation Examples With Excel Template Ordinary annuities and annuities due differ in the timing of those recurring payments. the future value of an annuity is the total value of payments at a future point in time. the present value is. For example, consider an annuity due with monthly payments of $1,000, an annual interest rate of 6%, and a duration of 5 years. first, convert the annual interest rate to a monthly rate (0.06 12 = 0.005). then, apply the modified formula: pv = $1,000 × [ (1 – (1 0.005)^ 60) 0.005] × (1 0.005). this calculation yields a present value. In this example, pmt= $1,000. r = 10%, represented as 0.10. n = 5 (one payment each year for five years) therefore, the present value of five $1,000 structured settlement payments is worth roughly $3,790.75 when a 10% discount rate is applied. if you simply subtract 10% from $5,000, you would expect to receive $4,500. This is different from a regular annuity, where payments are made at the end of each period. to calculate the future value of an annuity due, you can use the formula fv = p * ( (1 r)^ (n 1) 1) r, where p is the payment, r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods. real life examples of annuity due include car payments, mortgage.

Comments are closed.